Sep. 11, 2017
Toyota Develops New Hybrid Navigation and Voice Recognition Functions
as Part of Toyota's "Connected Strategy"
Functions Automatically Switch Between Cloud and On-board Computing
for Route Calculations and Location Searches
Toyota City, Japan, September 11, 2017―Toyota Motor Corporation (TMC) announces the development of hybrid navigation and voice recognition functions that operate through a combination of cloud computing and on-board computing, as part of Toyota's "connected strategy" based on DCM1 standard settings. Starting this autumn, Toyota will begin to roll out the new technologies in navigation systems (manufacturer option) installed in new models sold in Japan.
- Calculate and present faster routes to destinations
- Provide a larger selection of possible routes to choose from
- Offer greater flexibility in searching for destinations
- Make it easier to use voice command for multimedia systems
- Hybrid Functions
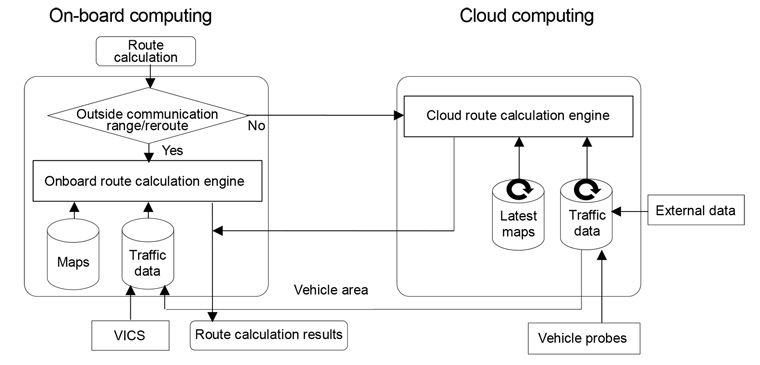
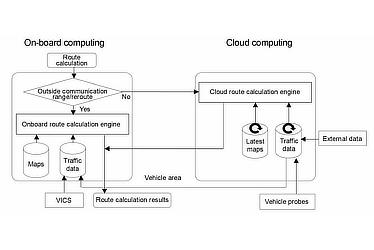
Toyota has developed the world's first2 hybrid navigation function. This function calculates driving routes and location searches in the cloud by tapping into databases that combine vehicle probe data3 gathered from other vehicles and external data. The driving routes and location search results are then transmitted to on-board devices. With its hybrid design, the function automatically switches to on-board computing when the vehicle is outside the range of communication networks or when faster processing is required for rerouting. (see Figure 1)
- Figure 1
- Hybrid navigation functions
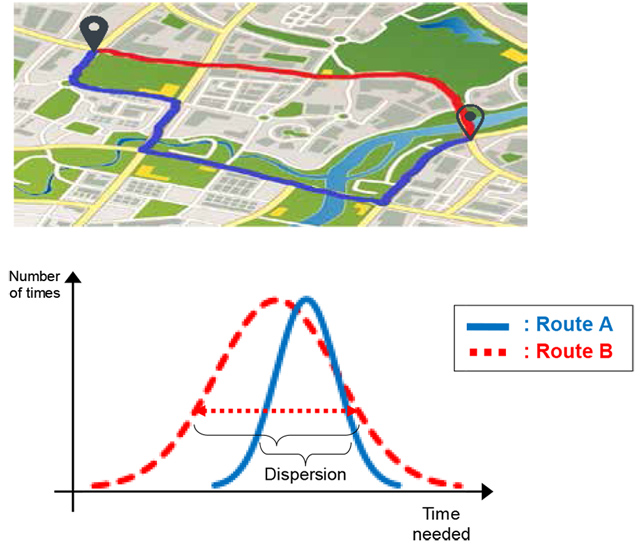
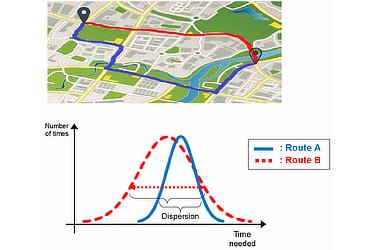
Cloud-based route calculations use driving time databases with compiled histograms of travel times for each road. These databases combine average driving time with dispersion data to calculate routes with the least driving time and to raise the precision of estimated arrival time. (see Figure 2)
- Figure 2
- Utilizing dispersion data for driving time
Driving time dispersion data raises the precision of estimated arrival time by designating routes based not only on the shortest average arrival time, but routes with a lower level of driving time dispersion.
- Route A
- Average driving time is longer, but dispersion is low.
- Route B
- Average driving time is short, but dispersion is high.
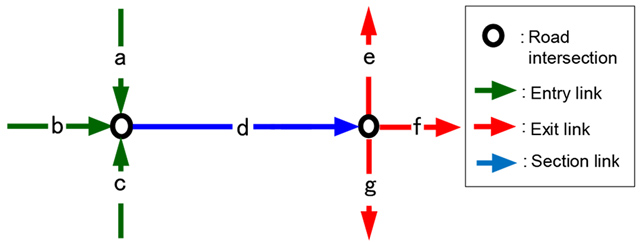
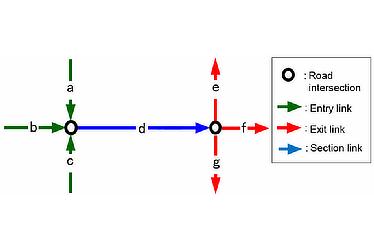
- Figure 3
- Combining entry and exit data for route sections
The calculations are based on three data links: section entry link, section link, and section exit link. For example, in Figure 3, the calculation for section link "d" uses nine types of data: three types of entry links (a, b, c) multiplied by three types of exit links (e, f, g).
Furthermore, cloud-based data processing makes it possible for Toyota to deliver the world's first2 "route expansion" function in which users can increase the types of routes used in the navigation system even after car purchase. Users can download new routes directly from the cloud. The first expansion route to be offered in Japan is the Kanto ETC 2.0 Toll Discount Priority Route.
For location searches, the new function enables broad searches using keywords or complex searches using multiple search terms. For example, the system can search for Himeji Castle by its nickname "Shirasagijyo" even if the word is mistakenly entered as "Shirosagijyo." Complex searches using such terms as "Ginza sushi" or "Akasaka French" are also possible.
- Hybrid Voice Recognition Function
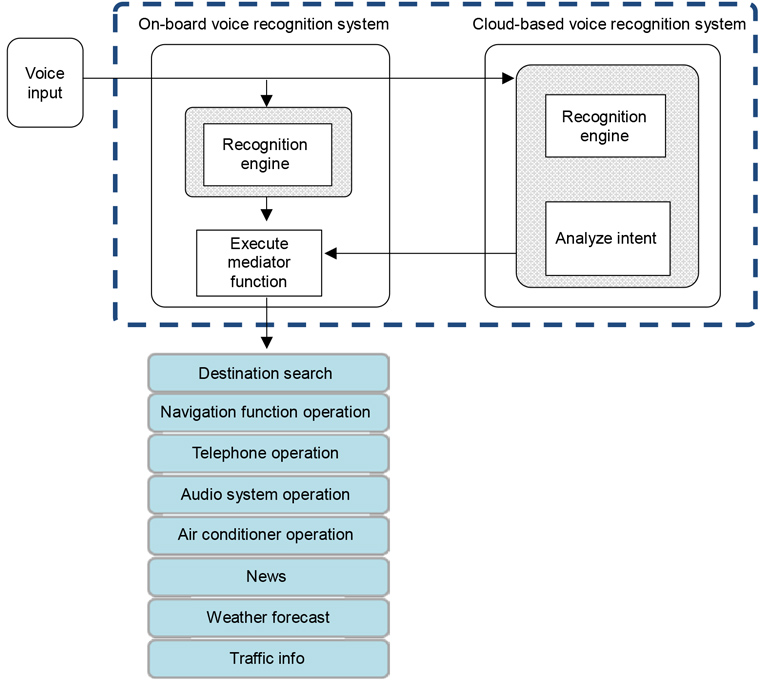
The hybrid voice recognition function has the advantage of using cloud computing to recognize natural speech and the names of a vast number of facilities, such as store names, as well as on-board computing to enable swift response to voice commands. The function switches automatically between the cloud and on-board computing based on the nature of the voice commands and the particular situation to ensure smooth voice operation of the multimedia systems.
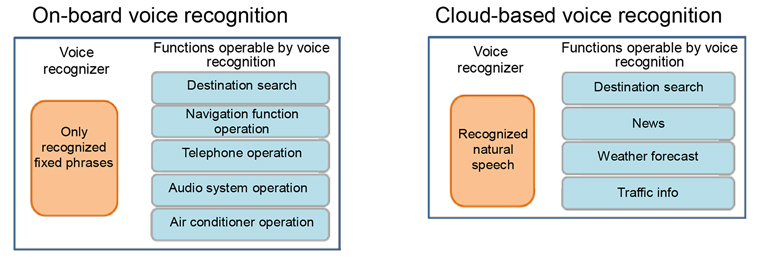
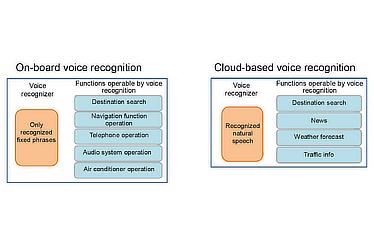
The voice recognition function is divided into two separate systems, on-board voice recognition and cloud-based voice recognition. While the previous cloud-based voice recognition system ("Agent" [an interactive voice response service]) recognized natural speech, the service was limited to destination searches, weather, news, and other server applications. Meanwhile, the capabilities of the on-board voice recognition system were limited to a set number of phrases. To search for an address, for example, the user had to say "Destination," "Address," "Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Koraku, 1 chome, 4" in this order. Users had to choose the system they wanted based on their purpose. (see Figure 4)
- Figure 4
- Previous voice recognition system
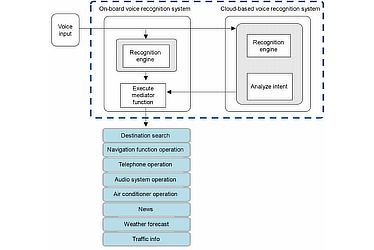
The newly developed hybrid voice recognition function automatically launches the relevant voice recognition system so that choosing a specific function is not required. The user simply expresses his or her need, such as "noodle shop with parking" or "set air conditioner to max" in natural speech to operate the systems. (see Figure 5)
- Figure 5
- Hybrid voice recognition system
1DCM: Data Communication Module
2According to TMC
3Collected from vehicles equipped with DCM