Feb. 26, 2018
Development of the New Powertrain Based on Toyota New Global Architecture (TNGA)
Using TNGA, Toyota has been changing the automobile from its very structure, lowering hood heights, lowering the center of gravity and implementing other innovations to improve driving performance. To enhance fundamental vehicle performance in terms of running, turning and stopping, it initiated a comprehensive review centered on vehicle platforms and is now, since the release of the fourth-generation Prius in 2015, expanding the use of new platforms throughout its product lineup. At the same time, it has been developing new powertrain units, which form the core of an automobile, that significantly improve both driving and environmental performance.
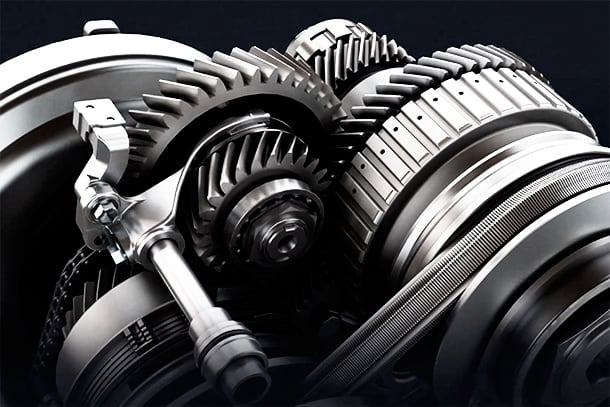
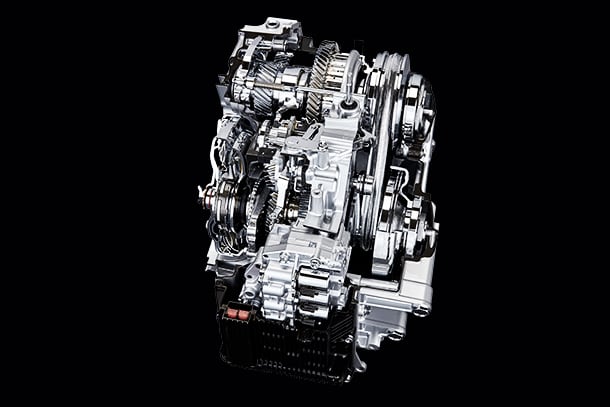
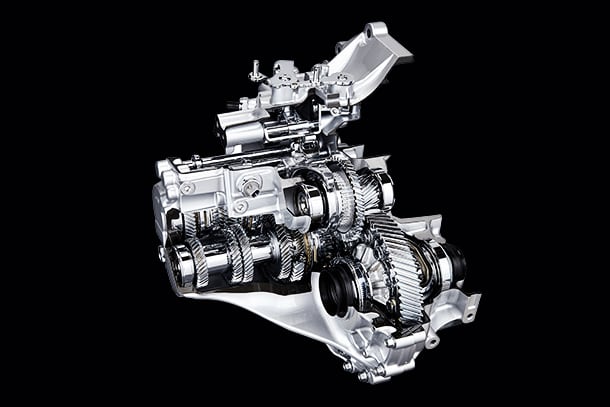
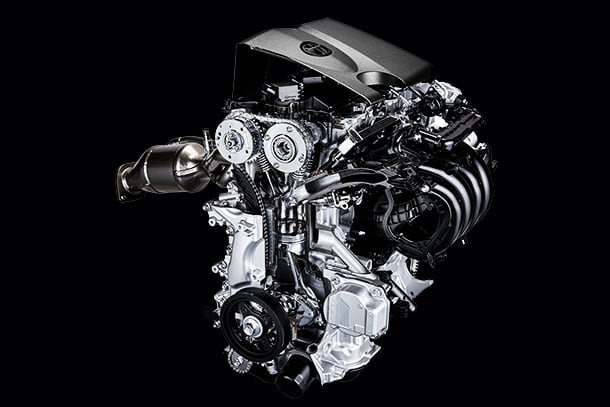
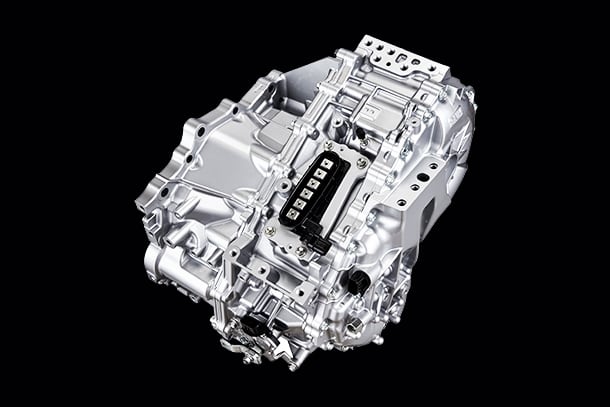
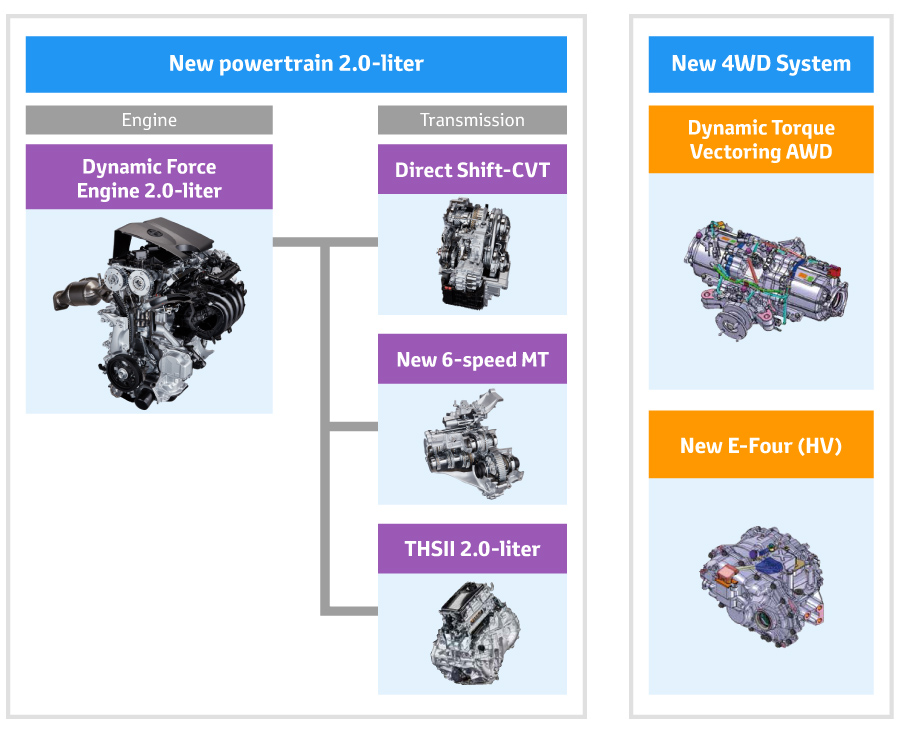
As part of the second step of the TNGA powertrain, which combines excellent driving performance and high environmental performance, a new powertrain series will be introduced to market.
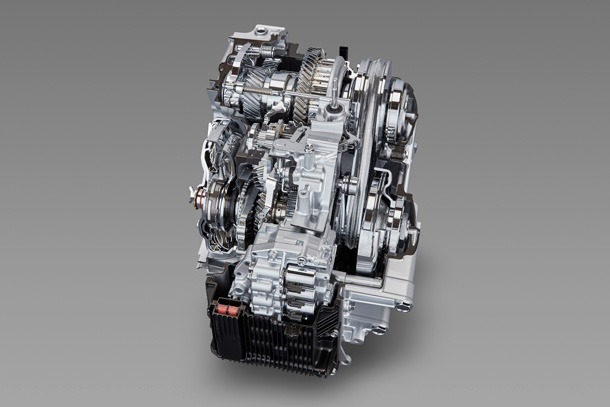
New powertrain
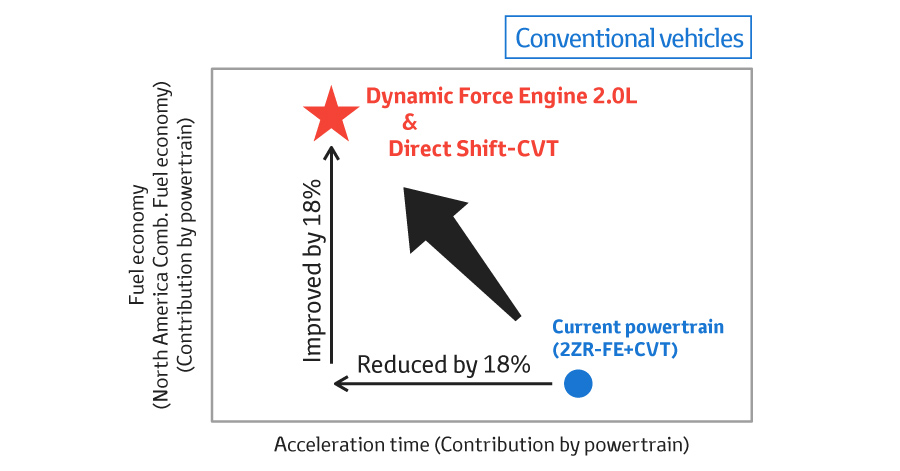
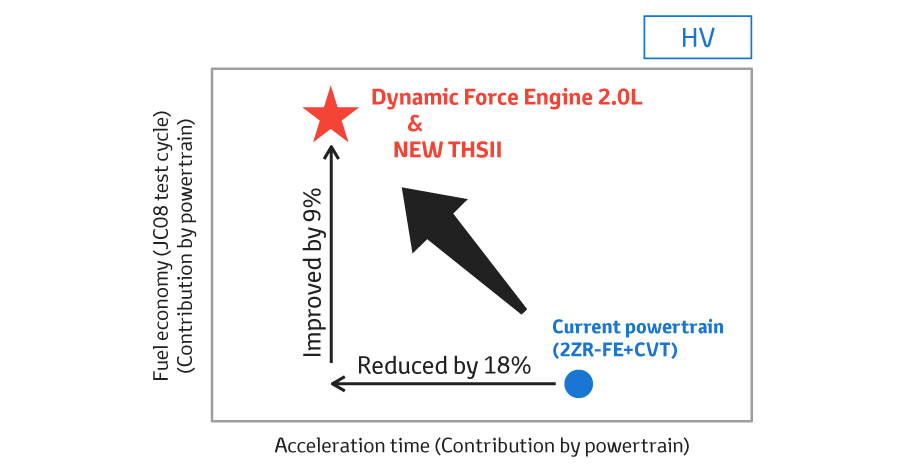
Environmental performance and Fun to Drive
New powertrain contributes to fuel economy and driving performance significantly.
New powertrain production technology
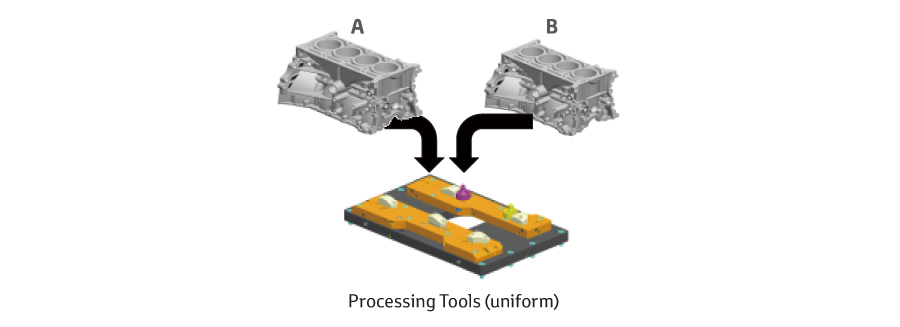
Develop lines that can flexibly produce different models at high speed by Uniform processing and assembly standards
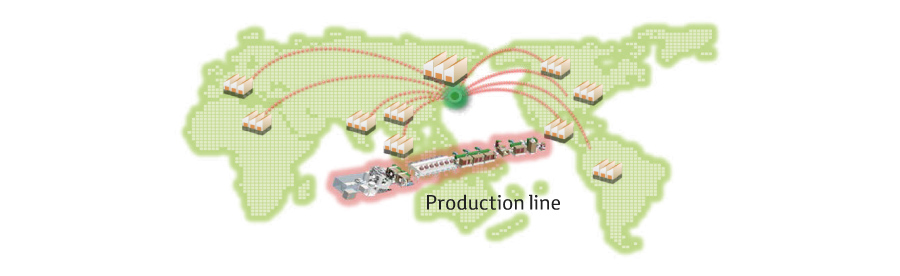
Accelerating global deployment with the standardization of process and facility specifications
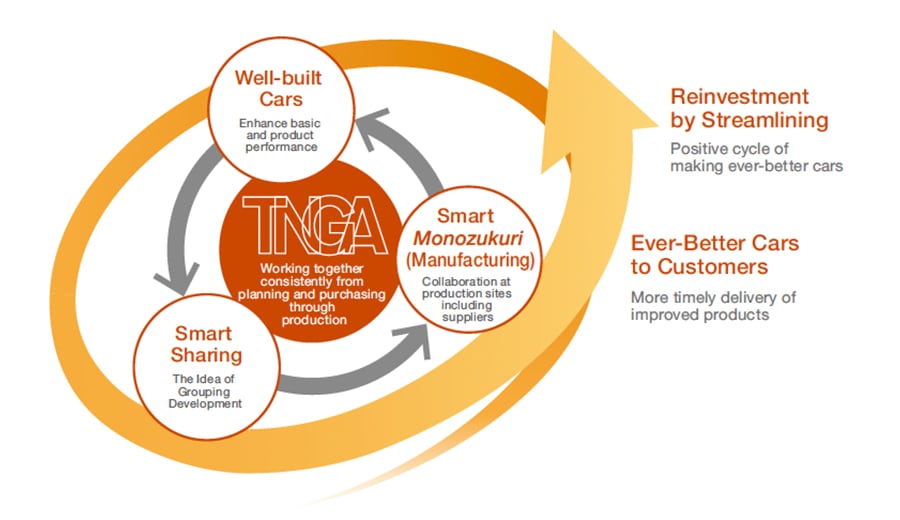
TNGA Cycle Accelerates Making Ever-Better Cars
The idea of TNGA cycle underlies the improved basic and product performance of Well-built Cars while incorporating smart sharing that considers total optimization, and promotes Smart Monozukuri (manufacturing) in collaboration with suppliers and production sites. This initiative has enabled a 20% reduction in development resources compared to the conventional ratio by reinvesting reserves to improve quality and product performance, leading to more timely delivery of ever-better cars.